Lt Breast and lumpectomy SIB 48/40Gy (RTOG 1005 arm2)
VMAT SX1
 |
Rx: 40Gy/15fx also 48Gy to Lumpectomy PTV (Simultaneous Integrated Boost)
RTOG 1005 Arm2-hypofractionation
1:42 VMAT treatment arc delivery time
 |
 |
Name (ID): ROQS-25, Breast-Simple (ROQS-25)
Plan or PlanSum ID: RTOG1005a2VF5
| Structure ID | Structure Code | Patient Structure | DVH Objective | Evaluator | Variation | Priority | Met | Achieved |
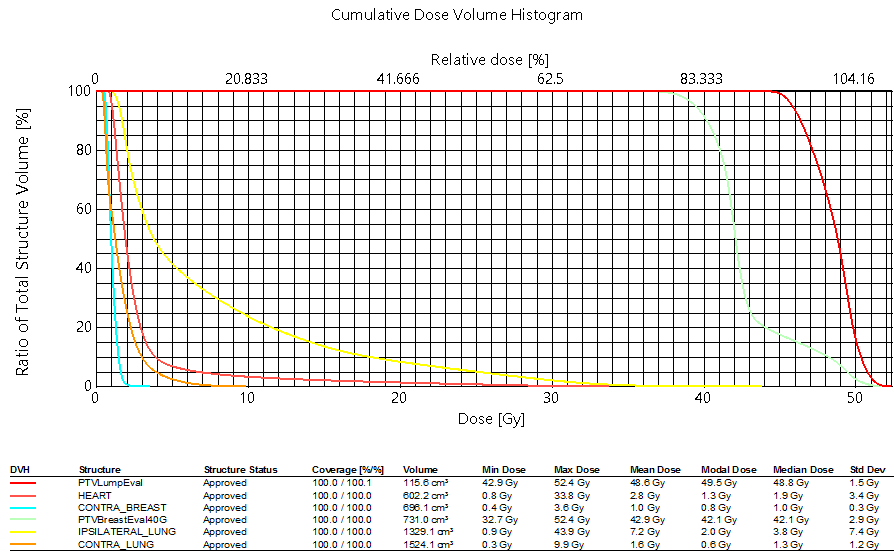
| BREAST PTV EVAL | PTVBreastEval40G | V38.0Gy[%] | >=95 | Goal | 99.06 % | |||
| BREAST PTV EVAL | PTVBreastEval40G | V36.0Gy[%] | >=90 | Goal | 99.92 % | |||
| BREAST PTV EVAL | PTVBreastEval40G | V48.0Gy[%] | <=30 | 35 | Goal | 10.64 % | ||
| BREAST PTV EVAL | PTVBreastEval40G | D50.0%[Gy] | <=43.2 | 44.8 | Goal | 42.106 Gy | ||
| WHOLE BREAST | PTV Breast - PTV | Max[Gy] | <=46 | 48 | Goal | 44.582 Gy | ||
| LUMPECTOMY PTV EVAL | PTVLumpEval | V45.6Gy[%] | >=95 | Goal | 96.62 % | |||
| LUMPECTOMY PTV EVAL | PTVLumpEval | V43.2Gy[%] | >=90 | Goal | 100.00 % | |||
| LUMPECTOMY PTV EVAL | PTVLumpEval | V52.8Gy[%] | <=5 | 10 | Goal | 0.00 % | ||
| LUMPECTOMY PTV EVAL | PTVLumpEval | Max[Gy] | <=55.2 | 57.6 | Goal | 52.382 Gy | ||
| CONTRALATERAL BREAST | CONTRA_BREAST | Max[Gy] | <=2.4 | 3.84 | Variation | 3.567 Gy | ||
| CONTRALATERAL BREAST | CONTRA_BREAST | D5.0%[Gy] | <=1.44 | 2.4 | Variation | 1.615 Gy | ||
| IPSILATERAL LUNG | IPSILATERAL_LUNG | V16.0Gy[%] | <=15 | 20 | Goal | 12.17 % | ||
| IPSILATERAL LUNG | IPSILATERAL_LUNG | V8.0Gy[%] | <=35 | 40 | Goal | 29.62 % | ||
| IPSILATERAL LUNG | IPSILATERAL_LUNG | V4.0Gy[%] | <=50 | 55 | Goal | 48.14 % | ||
| CONTRALATERAL LUNG | CONTRA_LUNG | V4.0Gy[%] | <=10 | 15 | Goal | 4.72 % | ||
| HEART | HEART | V8.0Gy[%] | <=10 | 15 | Goal | 4.12 % | ||
| HEART | HEART | Mean[Gy] | <=3.2 | 4 | Goal | 2.753 Gy | ||
| THYROID | THYROID | Max[Gy] | <=0.96 | 1.44 | Goal | 0.618 Gy |
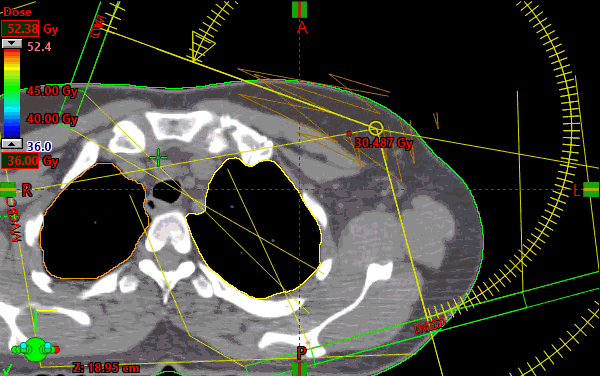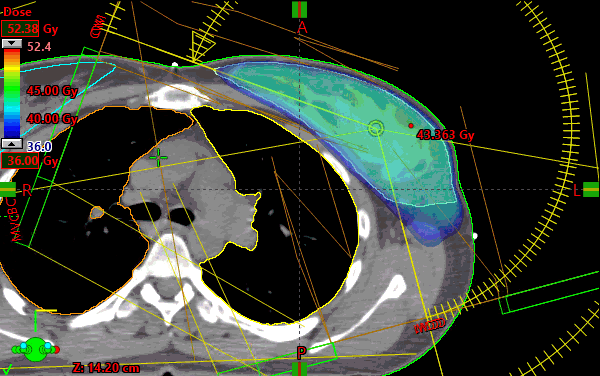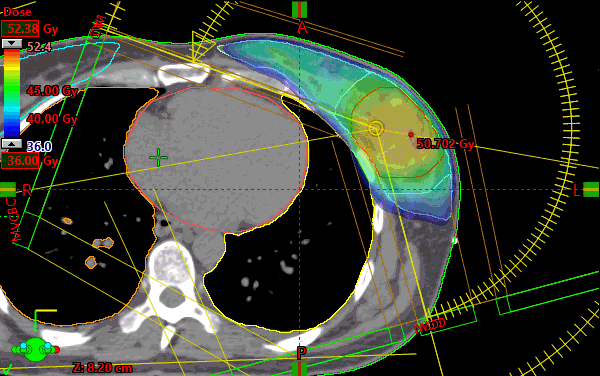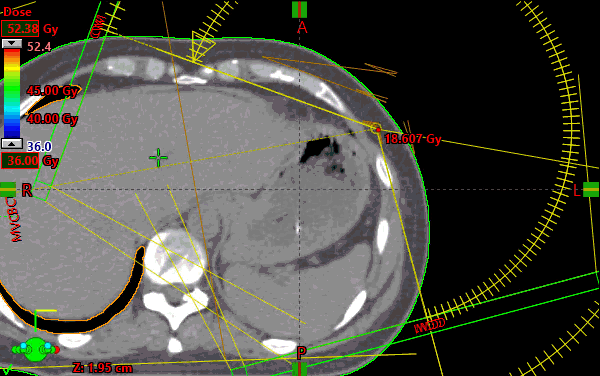
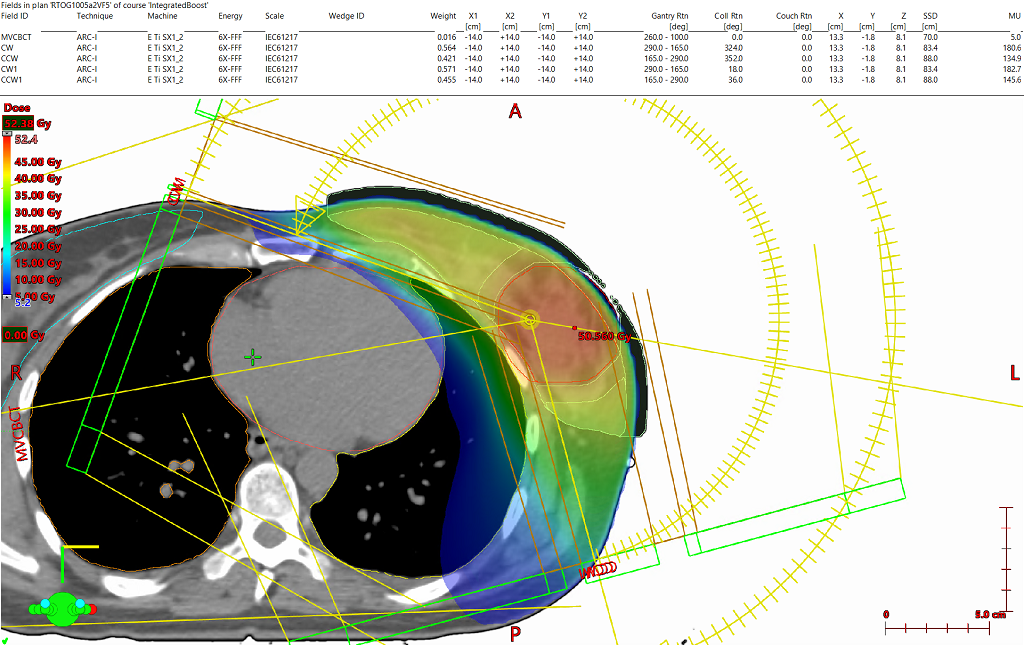
The plan consists of four (4) partial arcs set to begin just at the most medial aspect of the contralateral breast until 15 degrees from PA. The arcs’ unique collimator rotations were generated using the arc geometry tool.
Targets were defined as per RTOG1005. Ultimately the Lumpectompy PTV was used for optimization along with the BreastPTVeval with a 1cm expansion anteriorly and laterally (which consisted of .5cm expansion into air) called BreastPTVEvalOpt. A 1cm virtual bolus was created in Eclipse to provide density for the Photon Optimizer to dose the portion of the BreastPTVEvalOpt structure which extended beyond the patient’s Body contour. The obvious intention of this method was to create a VMAT plan which also provides .5cm of flash beyond the patient’s breast throughout the arc rotation. After optimization, the virtual bolus was unlinked from the plan and the dose was calculated (intermediate dose was not utilized).
To reach the planning goals of RTOG1005 arm2, higher than standard optimization priorities had to be placed to control the low dose to the heart, ipsilateral lung and the contralateral breast. There is usually a direct relationship between fully meeting the maximum point dose metric to contralateral breast and meeting the low dose sparing criteria in the ipsilateral lung (V4) and heart mean dose constraints. All protocol goals were met with minor deviations sited for the contralateral breast only.
With traditional C arm linear accelerators, static field IMRT is often employed for this SIB breast technique, as collimator rotations can be selected per field and fixed jaws placed to protect the heart and lung. When utilizing VMAT with traditional C arm linear accelerators in breast patients, it can be very difficult to meet the low dose sparring requirements as static collimator rotations are selected per arc which can cause the jaws to be larger than ideal as the gantry rotates around the patient. There are some more elaborate multiple smaller partial arc techniques which can be used to address this problem, but those techniques aren’t required with this system. Due to the dual stage stacked and staggered MLC design multiple collimator rotations can be selected and the arcs can be utilized to cover the entire treatment area without the problem of excess low dose to the patient’s heart and lungs from interleaf leakage due to the “per leaf jaw-tracking” effect of this MLC design. Less out of field dose is another advantage to using a FFF energy which also helps in meeting the very strict low dose OAR requirements of the RTOG 1005 protocol.
|
3rd party software plan report |
|
DICOM patient export |
Any reference to a "plan study" are simply what the organizers call each case and may not be a "study" in the FDA sense as they may not have been published in a peer reviewed journal.
Varian does not provide medical advice and these are illustrative examples only.
Leading plans by expert planner. Your results may vary.
FOR EDUCATIONAL AND SCIENTIFIC EXCHANGE ONLY – NOT FOR SALES OR PROMOTIONAL USE.