Prostate and lymph nodes 79.2/45Gy (RTOG 1115)
VMAT SX1
 |
Rx: 45Gy/25fx Initial plan to nodal volume with a 34.2Gy/19fx sequential boost to prostate+SV (79.2Gy)
RTOG 1115
2:33 boost VMAT treatment arc delivery time
 |
 |
Name (ID): Prostate_Nodes, Prostate_Nodes (ROQS_26)
Plan or PlanSum ID: BstSX1VMATID
| Structure ID | Structure Code | Patient Structure | DVH Objective | Evaluator | Variation | Priority | Met | Achieved |
| PTV_78 | PTV_78 | V34.2Gy[%] | >=98 | Goal | 99.26 % | |||
| PTV_78 | PTV_78 | D0.03cc[Gy] | <=36.6 | 37.6 | Goal | 36.508 Gy |
Name (ID): Prostate_Nodes, Prostate_Nodes (ROQS_26)
Plan or PlanSum ID: Plan Sum
| Structure ID | Structure Code | Patient Structure | DVH Objective | Evaluator | Variation | Priority | Met | Achieved |
| PTV_78 | PTV_78 | V79.2Gy[%] | >=98 | Goal | 99.31 % | |||
| PTV_45 | PTV_45 | V45.0Gy[%] | >=98 | Goal | 100.00 % | |||
| RECTUM | RECTUM | V75.0Gy[%] | <=15 | 20 | Goal | 7.85 % | ||
| RECTUM | RECTUM | V70.0Gy[%] | <=25 | 30 | Goal | 11.36 % | ||
| RECTUM | RECTUM | V65.0Gy[%] | <=35 | 40 | Goal | 14.61 % | ||
| RECTUM | RECTUM | V60.0Gy[%] | <=50 | 55 | Goal | 17.93 % | ||
| BLADDER | BLADDER | V80.0Gy[%] | <=15 | 85 | Goal | 6.07 % | ||
| BLADDER | BLADDER | V75.0Gy[%] | <=25 | 30 | Goal | 9.98 % | ||
| BLADDER | BLADDER | V70.0Gy[%] | <=35 | 40 | Goal | 12.73 % | ||
| BLADDER | BLADDER | V65.0Gy[%] | <=50 | 55 | Goal | 15.48 % | ||
| PENILE_BULB | PENILE_BULB | Mean[Gy] | <=52.5 | Goal | 7.420 Gy |
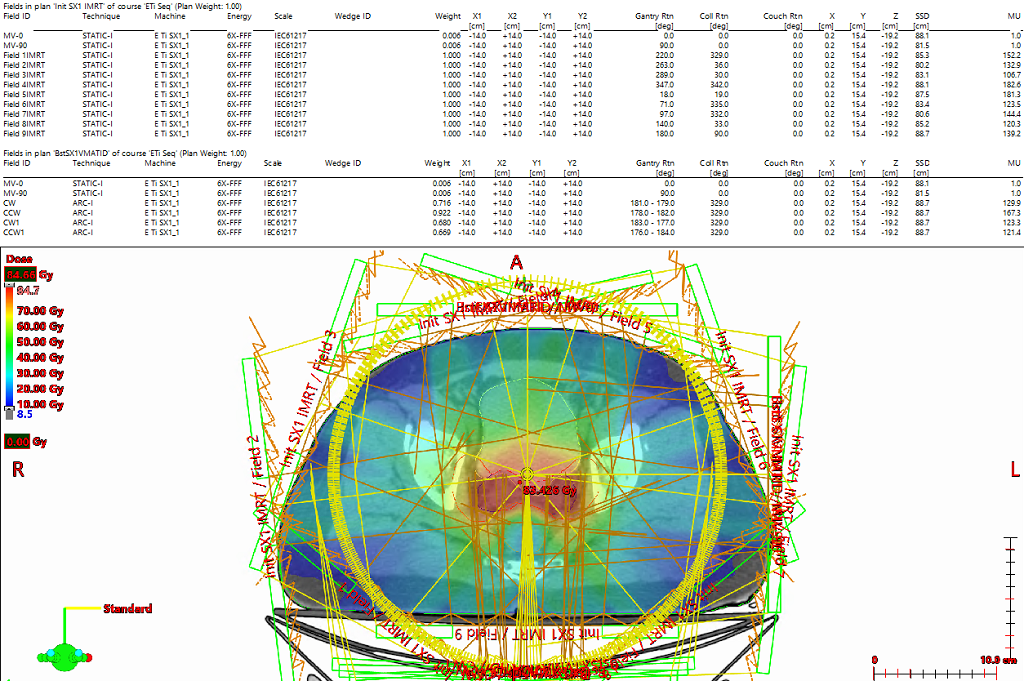
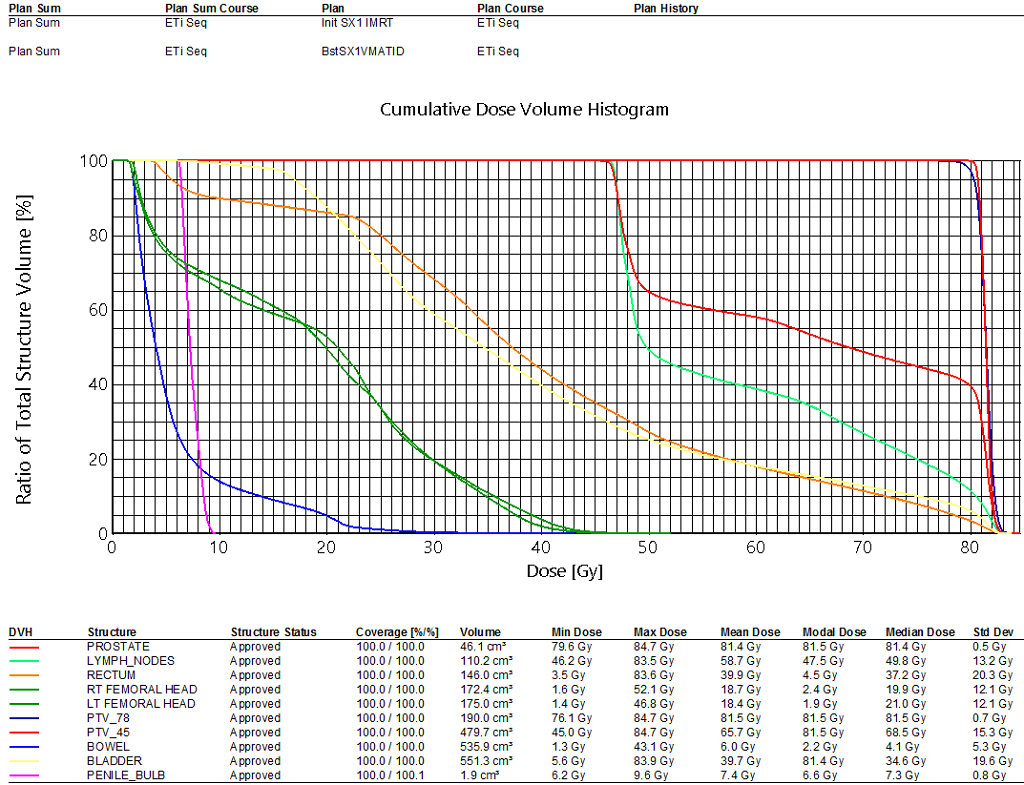
Prostate and nodes treated sequentially following RTOG 1115. Initial 9 field IMRT plan created with custom gantry positions to follow the irregular nodal volume target shape on the transverse planes. Beams were placed so edges created a sharp gradient against highest value OAR (rectum). Also, unique collimator rotations per field were selected from a beam's eye view to match the general angle of the target volume. All target coverage constraints were assessed separately in the initial plan and all were met.
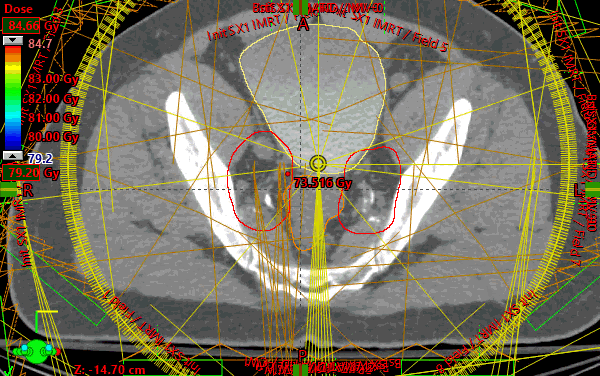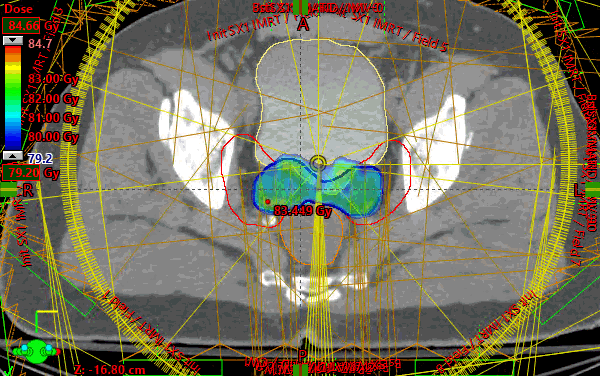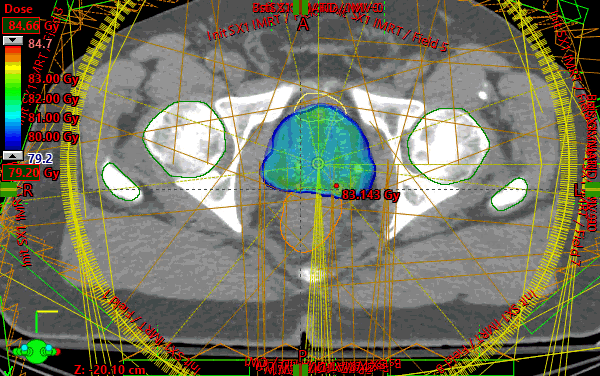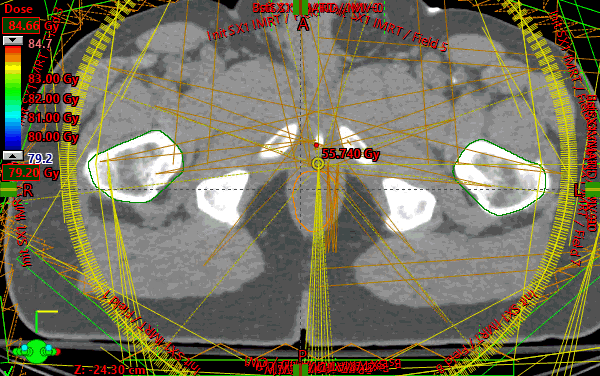
For the sequential boost, due to the round nature of the boost volume, VMAT technique was chosen and 4 almost complete arcs were used. Each arc used a different start and stop angle by 1 degree to stagger the available control points throughout each arc rotation. All target constraints were assessed separately in the boost plan and all were met. Finally, a plan sum was created to evaluate organs at risk and all the constraints were met. OAR goals were relatively easy to achieve in this case.
The challenge was achieving 98% target coverage while a maintaining a minimum target dose of 95% and not exceeding maximum dose of 107%. The temptation when a protocol enforces a minimum dose to the target is to simply perform a uniform expansion on the target and optimize on the expanded target. However, in this case, an optimization PTV was created and stretched outward only along the edges of the real PTV where the minimum dose was not met. Careful attention was paid to minimize stretching where the target interfaced/overlapped with an OAR (rectum).
Given the more complex target areas within the pelvis, this prostate plan shows a very reasonable delivery time for a IMRT pelvis and VMAT boost set up.
|
3rd party software plan report |
DICOM patient export |
Any reference to a "plan study" are simply what the organizers call each case and may not be a "study" in the FDA sense as they may not have been published in a peer reviewed journal.
Varian does not provide medical advice and these are illustrative examples only.
Leading plans by expert planner. Your results may vary.
FOR EDUCATIONAL AND SCIENTIFIC EXCHANGE ONLY – NOT FOR SALES OR PROMOTIONAL USE.